Sustainability in mixing head cleaning – now available in two versions
Sustainability is a key part of Henkel's corporate philosophy. That is why we focus on offering our customers sustainable solutions not only in the development of adhesives and sealants, but also in the development of mixing and dispensing machines.
Sonderhoff mixing and dispensing machines are sustainable because they use Formed-In-Place (Foam-Gasket) / FIP(FG) technology. In addition, the mixing chamber is cleaned of material residues using an ecological high-pressure water rinse.
Compared to conventional solvent rinsing, only tap water is used. Solvents, on the other hand, are not biodegradable and incur costs for purchase and disposal.
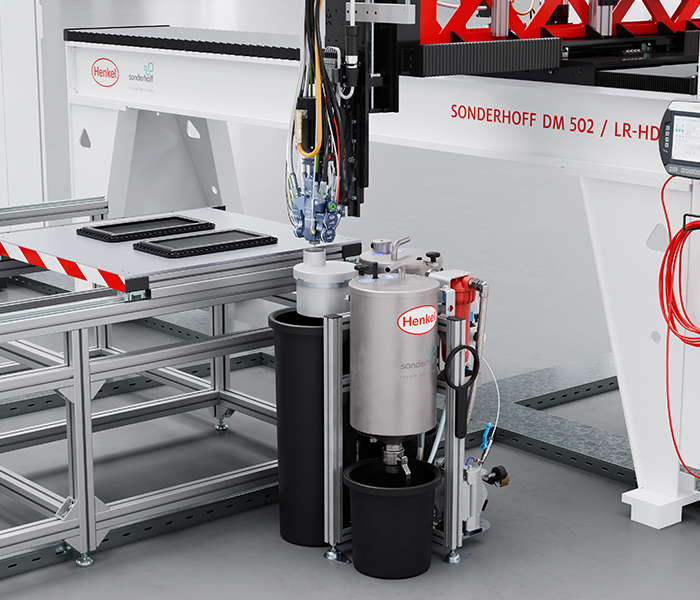


With the newly developed flushing water recycling system, the flushing/service water for high-pressure water flushing is cleaned in a two-stage filtration process. The filtered flushing water is then available as process water for several further flushing cycles.
This significantly reduces the fresh water consumption of high-pressure water flushing as well as the amount of water that has to be discharged into the sewage system or disposed of at a cost.
The cost savings achieved by using the flushing water recycling system allow the investment costs to be amortized after approximately 4.9 years, thus generating a return on investment.
The rinse water recycling system is available in two versions – stand-alone and electrically integrated. Both versions are installed in the mixing head's travel range and can be ordered as an option for mixing and dosing systems with LR-HD, LR-HE plus linear robots or 6-axis robots (not for 3E and SMART systems).

Sonderhoff Rinsing Water Recycling System
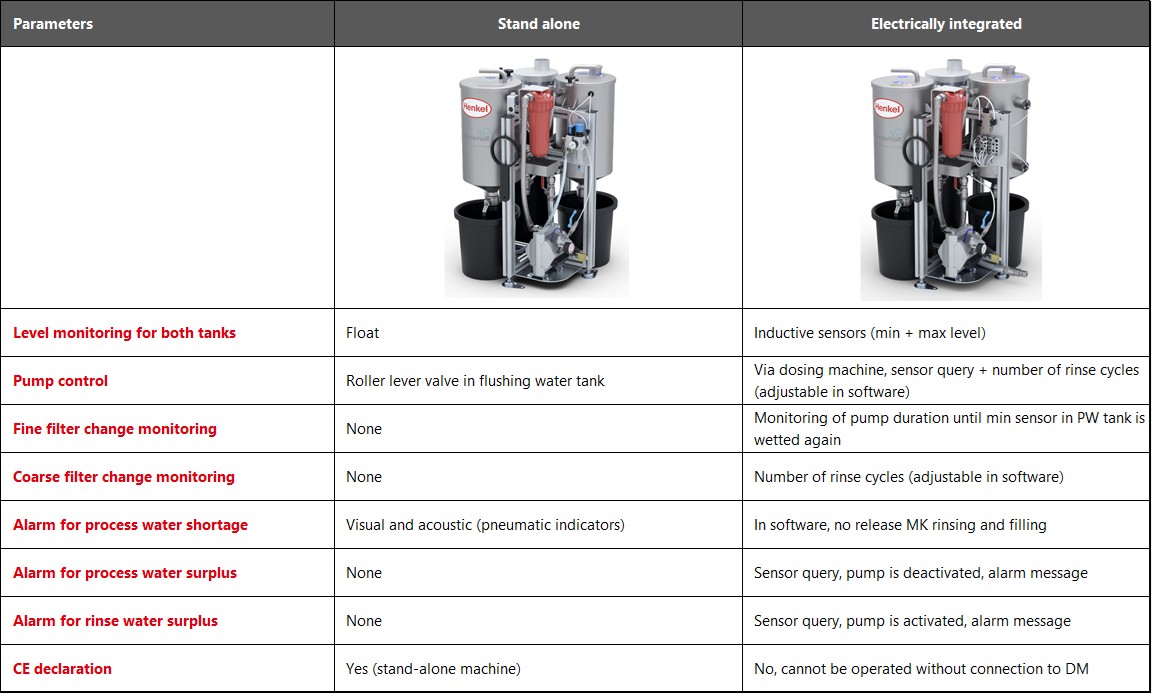
Comparison of the stand-alone version and the electrically integrated version
The process sequence of the rinsing water recycling system
The mixing chamber in the mixing head of the DM 50x dosing machine is cleaned using ecological high-pressure water rinsing (HDW), which uses approx. 2 x 200 ml of tap water per cleaning cycle, depending on the size of the mixing chamber and the material used. This is done by injecting water into the mixing chamber at an adjustable high pressure of between 80 and 140 bar, so that the surfaces in the mixing cham- ber are mechanically cleaned of material build-up.
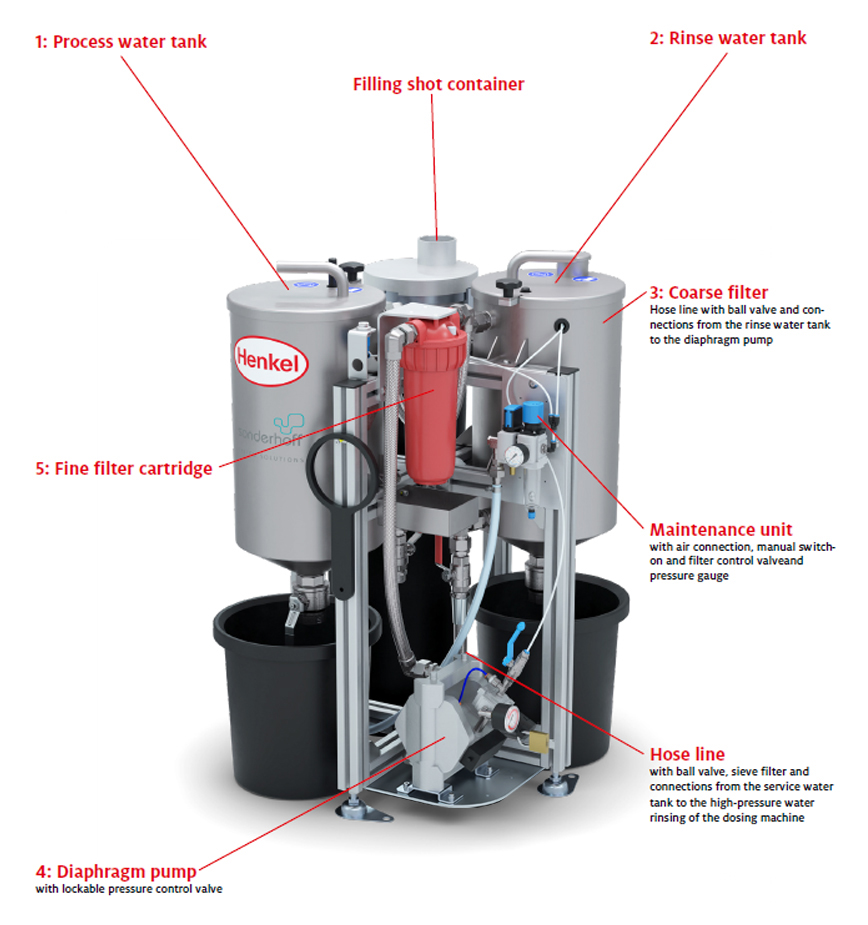
The process sequence of the rinse water recycling system for cleaning the process water for high-pressure water rinsing begins with filling the 25 litres process water tank (1) with tap water plus glycol 4 %. From there, the water is drawn in and the water used for this high-pressure cleaning is supplied to the mixing chamber via a hose.
The rinsing water used for this high-pressure cleaning is dispensed through the mixing head nozzle into the rinsing water tank (2). There, coarse impurities from the rinsing process of the mixing chamber are passed through a 50 µm coarse filter (3) in the first filter stage and filtered out.
When the water level in the rinse water tank (2) reaches a certain level after several rinsing processes, the roller lever valve is triggered by the integrated float and the pneumatic diaphragm pump (4) is activated.
The rinse water is then cleaned again by the second filter stage with a 5 µm fine filter cartridge (5) and pumped back into the process water tank (1).
The filtered process water is thus available for several further rinsing cycles. Depending on the number of rinsing cycles the 25 litres of fresh water in the rinse water recycling system must be changed approximately every 2 months.
If the water level in the process water tank (1) falls below a minimum level, a warning is issued via a visual and acoustic display.
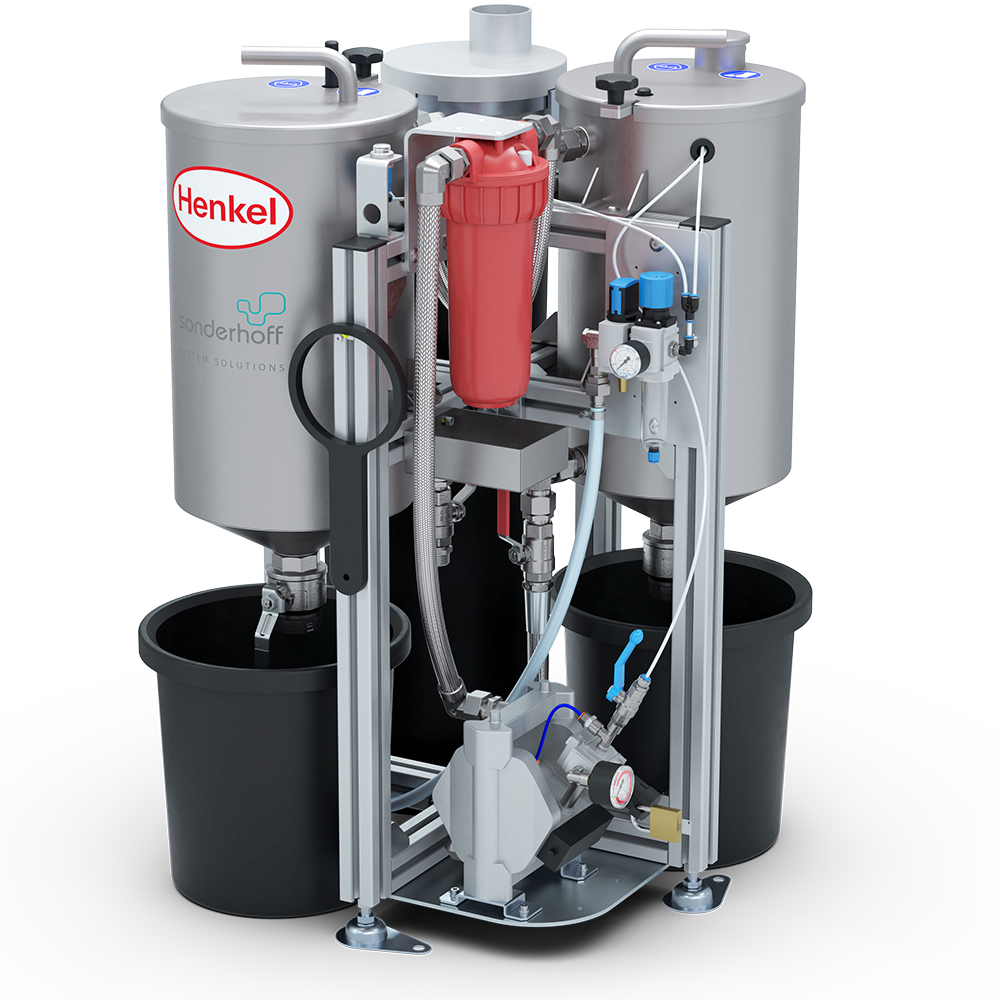 Process water tank
Process water tank
Diaphragm pump
Rinsing water tank
Coarse filter
Fine filter cartridge
Mixing head high-pressure water cleaning
Process water tank
Process water tank
Diaphragm pump
Rinsing water tank
Coarse filter
Fine filter cartridge
Mixing head high-pressure water cleaning
Process water tank
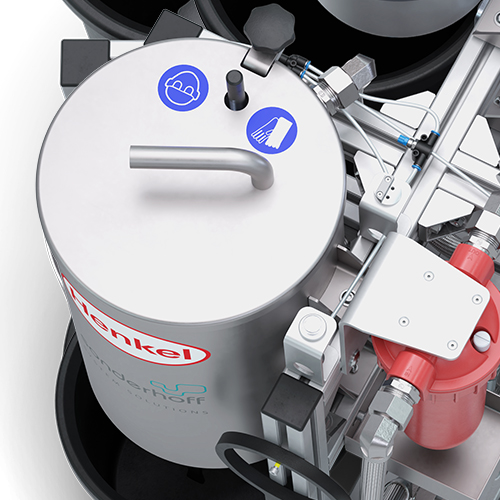

The finely filtered rinse water is pumped back into the process water tank as purified process water, where it is available for several more rinse cycles.
Process water tank
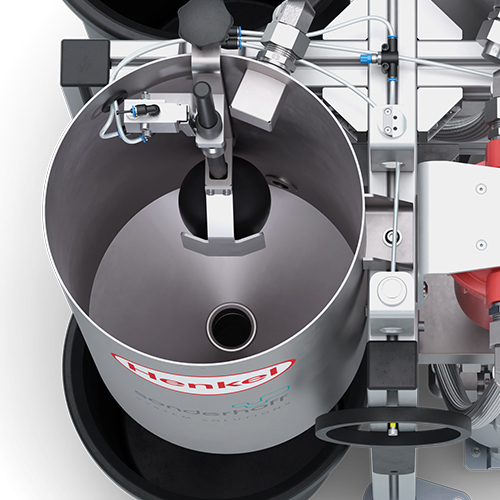
The process begins with filling of the 25 litres process water tank. From there, the water is sucked in and is supplied via a hose for the high-pressure water rinsing of the mixing chamber in the mixing head. If the water level in the process water tank falls below a minimum level, the float (B) activates the roller lever valve (A) and an audible and visual signal is emitted.
Diaphragm pump
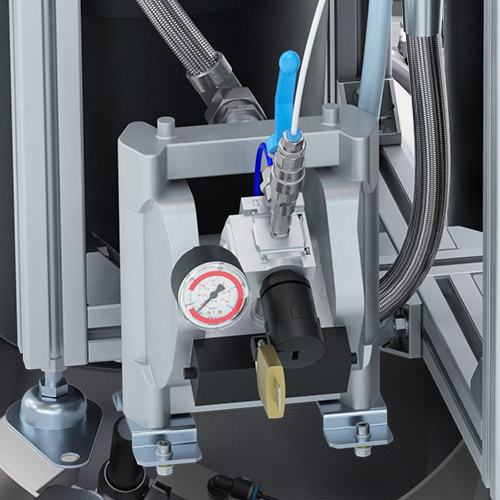
When the water level in the rinse water tank reaches a certain level after several rinsing processes, the roller lever valve is triggered by the integrated float and the pneumatic diaphragm pump is activated.
Rinsing water tank

The rinsing water used for high-pressure cleaning is dispensed through the mixing head nozzle into the rinse water tank.
Coarse filter

Coarse impurities from the rinsing process in the mixing chamber are passed through a 50 μm coarse filter in the rinsing water tank in the first filter stage and filtered out.
Fine filter cartridge

The coarsely filtered rinsing water, activated by the membrane pump, is fed to the second filter stage and purified there with a 5 μm fine filter cartridge.
Mixing head high-pressure water cleaning
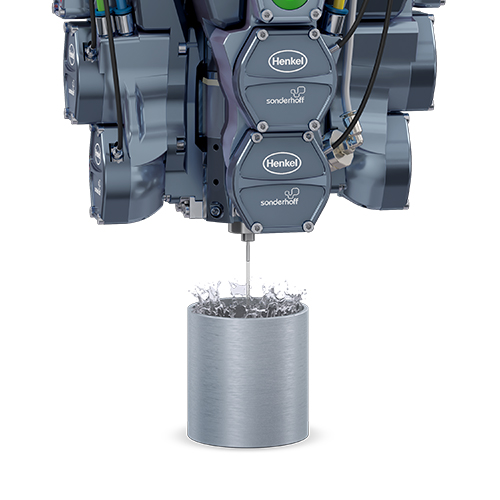

With ecological high-pressure water rinsing (HDW), the mixing chamber in the mixing head is cleaned by injecting (approx. 2 x 200 ml per cleaning cycle, depending on the size of the mixing chamber and the material used) at an adjustable high pressure. material used) at an adjustable high pressure of between 80-140 bar.
Cost savings when using the Rinsing Water Recycling System
Initial situation for the customer‘s work process:
|
Working days per year (5 days per week) |
253 |
|
Shifts per day |
2 |
|
Rinsing cycles per shift |
20 |
|
Water per rinse cycle |
400 ml |
|
Disposal costs per tonne |
800 € |
|
|
Without rinse water recycling system | With rinse water recycling system |
|
Water consumption / year |
4,048 l | 120 l |
|
Disposal costs for contaminated water (litres) / year |
3,200 € | |
|
Disposal costs for contaminated water, filter + filter cake / year |
96.00 € | |
|
Costs per fresh water litre / year |
12.15 € | 0.36 € |
|
Labour costs / year |
675 € | 180 € |
|
Filter and glycol additive purchase |
60 € | |
|
Total |
3,887.15 € | 335.36 € |
|
Savings / year (Y) |
3,550.79 €/Y |
FAQ rinsing water recycling system
What is the maximum distance between the process water tank of the Sonderhoff rinse water recycling system and the HDW (maximum hose length)?
10 m
Which robots are compatible with the stand-alone/electrically integrated rinse water recycling system?
6-axis robot, 3-axis linear robots LR-HD, LR-HE plus
Which robots does the SMART rinsing water recycling system work with?
Only with the SMART version of the dosing machine
No, it is a stand-alone version without sensors or PLC connections.
Which versions of the rinsing water recycling system can communicate with or be controlled by our dosing machines?
a) Electrically integrated rinsing water recycling system
b) SMART rinsing water recycling system
Can the rinse water recycling system communicate with or be controlled by our dosing machines?
No, it is a self-sufficient stand-alone version without sensors or PLC connections.
Can the rinse water recycling systembe retrofitted to existing dosing machines?
Yes, usually for the mixing and dosing systems with 3-axis linear robots LR-HD, LR-HE plus or 6-axis robots (this does not apply to the 3E and SMART systems), provided the existing system layout offers sufficient space.
With which chemicals can the rinse water recycling system NOT be used?
a. Water-soluble adhesives and sealants
b. Very low viscosity (<1000 mPas) materials with a high isocyanate content (>40%) (reacts very quickly with water)
c. Filled materials that are still very liquid after dosing/mixing (<1000 mPas)
What connections does the rinse water recycling system require?
Only compressed air (max. 8 bar) and the connecting hose for water from the process water tank to the HDW (see flow chart in the manual).
How must the rinse water recycling system be set up as a stand-alone/electrically integrated unit?
The rinse water recycling system replaces the normal filling station and must be positioned so that cleaning with HDW can take place in the rinse water tank and the filling shots can be made in the filling
How often does fresh water need to be refilled?
It is recommended to check the water level in both tanks once a week. If the water level in the process water tank is less than half full and there is hardly any water left in the rinse water tank, water must be refilled. If the rinse water tank is almost empty, the process water tank can be filled up to the maximum level mark.
Under what conditions can the rinse water recycling system not be used? (Exclusion criteria)
a. See 5.
b. Dosing machine in 3E cell
c. HDW positioned more than 1 m above the rinse water recycling system Minimum water level in the process tank (HDW suction capacity is then insufficient)
d. Distance between HDW and rinsing water recycling system >8m
Is the rinsing water recycling system height-adjustable?
The rinsing water recycling system itself is not height-adjustable, but the injection nozzle can be pulled out by a maximum of 100mm using a knurled screw to facilitate alignment with the dosing head. If this is not sufficient, the rinse water recycling system must be placed on a platform.
Is the rinse water recycling system mobile?
No, once it has been positioned, it should be secured to the floor with heavy-duty anchors.
Does the water in the rinse water recycling system need to be replaced?
Yes, despite the addition of glycol, algae may form in the water due to contamination or it may otherwise become “bad” (e.g., start to smell). It is therefore recommended that the water in the entire system be replaced at least 3-4 times a year to prevent the fine filter from clogging.
Can the volume of the acoustic signal for the process water tank be changed?
Yes, the volume can be adjusted using the throttle located near the acoustic signal.
How can you tell when there is not enough water in the process water tank?
The visual and acoustic indicators on the frame of the rinse water recycling system signal when there is too little water in the process water tank. The visual signal turns red and the acoustic indicator emits a whistling sound (the volume can be adjusted). In the two electrically integrated versions, a warning message is displayed on the HMI of the dosing machine.
